Deterministic proposals
Outline
Topics
- Deterministic proposals
- Involutions
- Proposal Jacobian determinants
Rationale
In our first exposure to MH, we defined the proposal as a probability distribution \(q(\cdot|x)\) based on the current point \(x\).
For HMC, it is more natural to consider the proposal as a deterministic function \(T(x)\) (namely, as we saw, the proposal is to “let the ball roll the ball a little bit”).
We state a version of the MH algorithm based on such deterministic proposal here.
MH with deterministic proposals
Algorithm:
- Denote the current state by \(x \in \mathbb{R}^d\)
- Propose: \(x^* = T(x)\) for some deterministic proposal mapping \(T : \mathbb{R}^d \to \mathbb{R}^d\)
- Assume that \(T\) satisfies \(T = T^{-1}\).
- Terminology: \(T\) is an involution.
- Compute the ratio, \[r(x) = \frac{\gamma(x^*)}{\gamma(x)} | \nabla T(x) |,\] where \(| \nabla T(x) |\) denotes the Jacobian determinant.
- Accept \(x^*\) with probability \(\alpha(x) = \min(1, r(x))\), otherwise stay at \(x\).
Calculus review: do you remember what is the Jacobian determinant?
\[\begin{align*} \nabla T(x) &= \begin{bmatrix} \dfrac{\partial T_1}{\partial x_1} & \cdots & \dfrac{\partial T_1}{\partial x_n}\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ \dfrac{\partial T_m}{\partial x_1} & \cdots & \dfrac{\partial T_m}{\partial x_n} \end{bmatrix} \\ |\nabla T(x)| &= |\det \nabla T(x)|. \end{align*}\]
Proposition: (Tierney, 1998) if \(T\) is a continuously differentiable involution, then the above algorithm is \(\pi\)-invariant.
Examples of involution
Swaps:
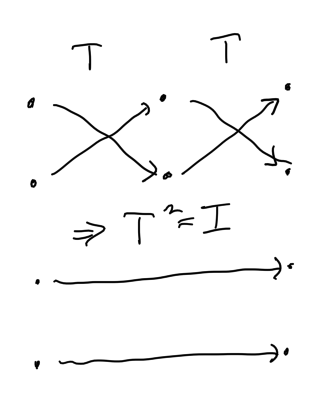
- Set \(T(x_1, x_2) = (x_2, x_1)\).
- To show involution, compute \(T^2(x) = T(T(x))\) and show \(T^2 = I\), the identity map.
- \(T(T(x_1, x_2)) = T(x_2, x_1) = (x_1, x_2)\) ✅
Multiplicative proposal: complete the definition of \(T\) to make it an involution on \(\mathbb{R}\times \mathbb{R}^+\). \[T(x_1, x_2) = T(x, m) = (mx, \_\_).\]
Question: Compute the Jacobian determinant of the multiplicative proposal involution.
You should get a triangular matrix i.e. in our context of the form
\[\begin{align*} \nabla T &= \begin{bmatrix} a_{11} & a_{12} \\ 0 & a_{22} \end{bmatrix}. \end{align*}\]
Now recall that from properties of triangular matrices, this means that to compute it determinant, you just have to compute the product of the diagonal entries, \(\det \nabla T = a_{11} a_{22}\).
References
- See Tierney, 1998 for the introduction of the notion of involutions and deterministic proposals to the MCMC literature.
- See Green, 1995 for early use of the multivariate change of variable formula in MH acceptance ratios.